Geological Timescale
pyrolite includes a simple geological timescale, based on a recent verion
of the International Chronostratigraphic Chart 1. The
Timescale class can be used to look up names for
specific geological ages, to look up times for known geological age names
and to access a reference table for all of these.
- 1
Cohen, K.M., Finney, S.C., Gibbard, P.L., Fan, J.-X., 2013. The ICS International Chronostratigraphic Chart. Episodes 36, 199–204.
First we’ll create a timescale:
From this we can look up the names of ages (in million years, or Ma):
ts.named_age(1212.1)
/home/docs/checkouts/readthedocs.org/user_builds/pyrolite/checkouts/main/pyrolite/util/time.py:261: FutureWarning: Series.__getitem__ treating keys as positions is deprecated. In a future version, integer keys will always be treated as labels (consistent with DataFrame behavior). To access a value by position, use `ser.iloc[pos]`
max([ix for (ix, r) in enumerate(counts) if r == counts[0]])
/home/docs/checkouts/readthedocs.org/user_builds/pyrolite/checkouts/main/pyrolite/util/time.py:54: FutureWarning: Series.__getitem__ treating keys as positions is deprecated. In a future version, integer keys will always be treated as labels (consistent with DataFrame behavior). To access a value by position, use `ser.iloc[pos]`
nameguess = agenamelist[-1]
'Ectasian'
As geological age names are hierarchical, the name you give an age depends on what level you’re looking at. By default, the timescale will return the most specific non-null level. The levels accessible within the timescale are listed as an attribute:
['Eon', 'Era', 'Period', 'Superepoch', 'Epoch', 'Age']
These can be used to refine the output names to your desired level of specificity (noting that for some ages, the levels which are accessible can differ; see the chart):
ts.named_age(1212.1, level="Epoch")
'Ectasian'
The timescale can also do the inverse for you, and return the timing information for a given named age:
ts.text2age("Holocene")
(0.0117, 0.0)
We can use this to create a simple template to visualise the geological timescale:
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, figsize=(5, 10))
for ix, level in enumerate(ts.levels):
ldf = ts.data.loc[ts.data.Level == level, :]
for pix, period in ldf.iterrows():
ax.bar(
ix,
period.Start - period.End,
facecolor=period.Color,
bottom=period.End,
width=1,
edgecolor="k",
)
ax.set_xticks(range(len(ts.levels)))
ax.set_xticklabels(ts.levels, rotation=60)
ax.xaxis.set_ticks_position("top")
ax.set_ylabel("Age (Ma)")
ax.invert_yaxis()
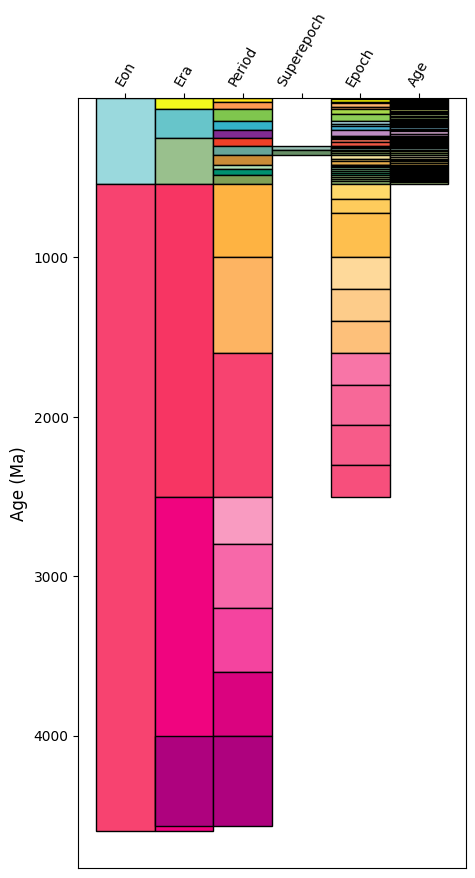
This doesn’t quite look like the geological timescale you may be used to. We can improve
on the output somewhat with a bit of customisation for the positioning. Notably, this is
less readable, but produces something closer to what we’re after. Some of this may soon
be integrated as a Timescale method, if there’s interest.
import numpy as np
from matplotlib.patches import Rectangle
# first let's set up some x-limits for the different timescale levels
xlims = {
"Eon": (0, 1),
"Era": (1, 2),
"Period": (2, 3),
"Superepoch": (3, 4),
"Epoch": (3, 5),
"Age": (5, 7),
}
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, figsize=(4, 10))
for ix, level in enumerate(ts.levels[::-1]):
ldf = ts.data.loc[ts.data.Level == level, :]
for pix, period in ldf.iterrows():
left, right = xlims[level]
if ix != len(ts.levels) - 1:
time = np.mean(ts.text2age(period.Name))
general = None
_ix = ix
while general is None:
try:
general = ts.named_age(time, level=ts.levels[::-1][_ix + 1])
except:
pass
_ix += 1
_l, _r = xlims[ts.levels[::-1][_ix]]
if _r > left:
left = _r
rect = Rectangle(
(left, period.End),
right - left,
period.Start - period.End,
facecolor=period.Color,
edgecolor="k",
)
ax.add_artist(rect)
ax.set_xticks([np.mean(xlims[lvl]) for lvl in ts.levels])
ax.set_xticklabels(ts.levels, rotation=60)
ax.xaxis.set_ticks_position("top")
ax.set_xlim(0, 7)
ax.set_ylabel("Age (Ma)")
ax.set_ylim(500, 0)
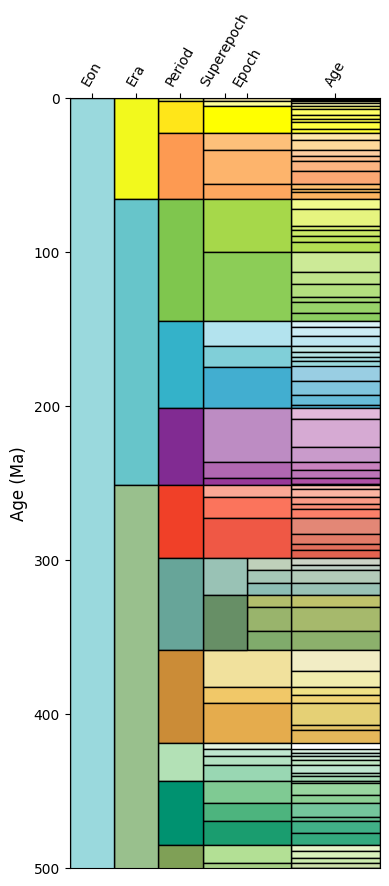
(500.0, 0.0)
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 2.035 seconds)